Auswirkung des Klimawandels auf die Wasserverfügbarkeit – Anpassung an Trockenheit und Dürre in Deutschland (WADKlim)
Abschlussbericht
- Publication
- Citation
Stein, Ulf et al. 2024: Auswirkung des Klimawandels auf die Wasserverfügbarkeit − Anpassung an Trockenheit und Dürre in Deutschland (WADKlim). Abschlussbericht. Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau. UBA TEXTE 143/2024
As climate change progresses, Germany faces increasing challenges in terms of water availability. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns lead to more frequent and more intense dry periods, which in turn cause falling groundwater levels and decreasing soil moisture. The "WADKlim" research project, carried out on behalf of the German Federal Environment Agency, examined the effects of these changes and developed strategies for adapting to water scarcity and drought. The project's final report provides valuable insights into current and future water availability in Germany and identifies possible solutions.
Analysis of water availability
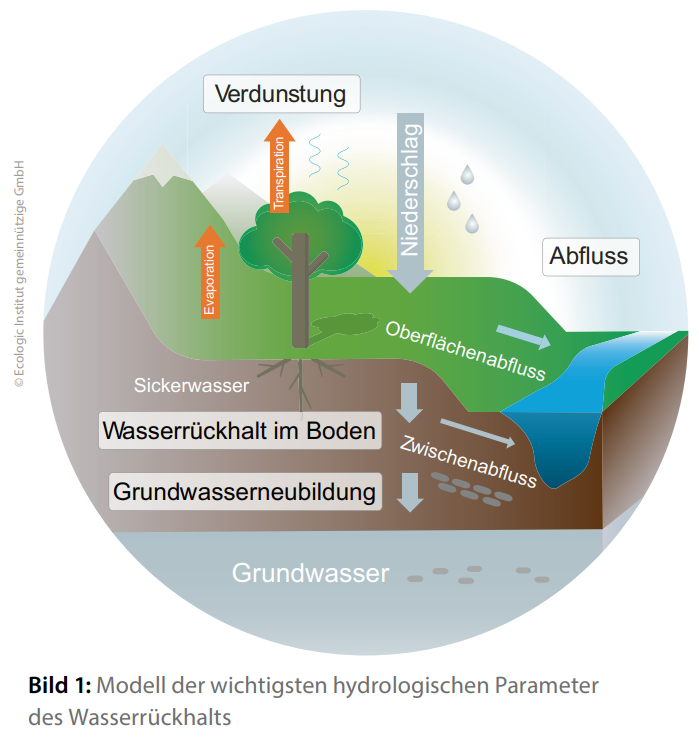
The research results of the WADKlim project reveal regional differences in the development of water availability in Germany. Over the past 20 years, the distribution and mean values of annual groundwater recharge have changed significantly, particularly in western and southern Germany. Prolonged periods of groundwater droughts have become evident. In the future, groundwater management will continue facing recurring and persistent phases of groundwater droughts.
Addressing water use conflicts
Another key topic of the final report is the management of water use conflicts. Such conflicts arise when water demand exceeds supply, which becomes particularly problematic in times of drought and aridity. The WADKlim project identified regions where such conflicts occur with particular frequency and developed measures to reduce them. These include promoting water reuse in urban areas, developing water supply concepts and establishing regional exchange bodies such as water advisory councils. These advisory boards are intended to serve as a platform for exchange between different stakeholders and help to identify and resolve conflicts at an early stage.
Recommended measures and future actions
The final report of the WADKlim project emphasizes the urgency of implementing adaptation measures at an early stage to mitigate the effects of climate change on water availability. Recommended measures include improving water use efficiency, promoting water reuse technologies in urban areas and developing comprehensive water supply concepts. In addition, the importance of further research and systematic monitoring is emphasized in order to better predict and respond to future developments. The knowledge gained and strategies developed in the project provide a valuable basis for political decisions and contribute to the sustainable management of water resources in Germany.
Conclusion
The final report of the WADKlim project shows how climate change affects water availability in Germany and what measures are needed to meet these challenges. Combining analysis of scientific literature, modeling and the development of practical solutions, the report offers valuable ideas for dealing with water scarcity and water use conflicts. The implementation of further measures, such as water retention in the countryside, will be crucial to mitigate the effects of climate change in Germany.
Further information is available on the UBA website
Additional information and documents are available on the website of the German Environment Agency (UBA). In addition to the appendix to the report on Drought and Water Use Conflicts in Germany (WADKlim), various catalogs of measures and the results of the extensive literature research can also be viewed there. These supplementary materials provide valuable in-depth information and support the practical implementation of the measures described in the report.