Sustainable Building
A Case Study on Concrete Recycling in France
- Publication
- Citation
Duin, Laurens and Aaron Best 2018: Sustainable Building: A Case Study on Concrete Recycling in France, Ecologic Institute: Berlin.
This case-study paper focuses on concrete recycling in France as a means of understanding circular-economy transitions in the building-materials sector. The EU, including France, produces large volumes of construction and demolition waste (CDW) per year and aims to increase the re-use of these materials, reducing landfilling and negative environmental impacts. Recycling concrete is seen as a way to contribute to these objectives by ensuring that a portion of this waste is turned into a product with value. Currently, France does not recycle CDW as much as some other Member States. This case study paper carries out a scenario analysis comparing two future scenarios for 2030, providing insights into important environmental and economic impacts of an increased concrete recycling rate in France.
- Language
-
English
- Authorship
-
Laurens Duin
- Credits
With contributions by: Marius Hasenheit (Ecologic Institute)
- Funding
-
European Commission, Executive Agency for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (EASME), International - Year
- Dimension
- 59 pp.
- Project
- Project ID
- Table of contents
-
Click to show full table of contents
Executive Summary
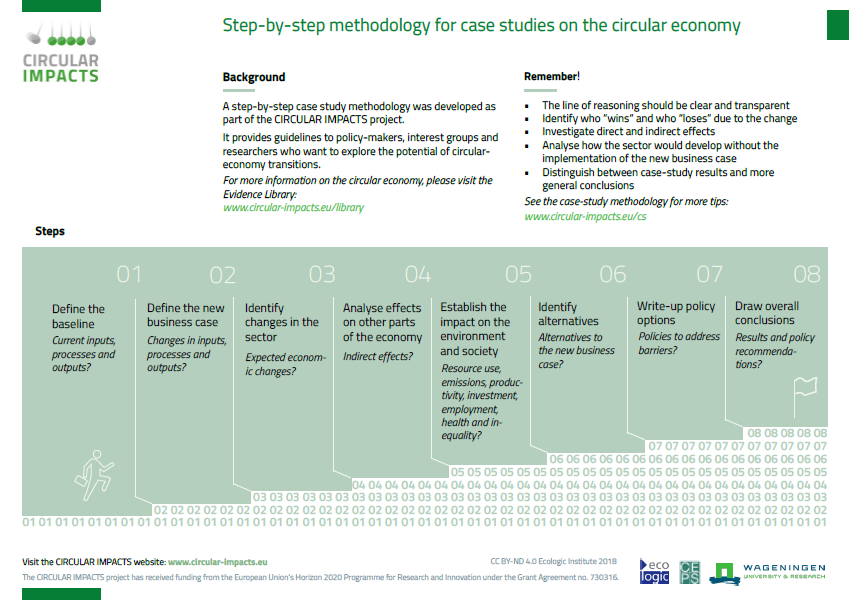
1 :: Introduction
2 :: Step 1: Defining the Baseline
2.1 The role of concrete in Europe
2.1.1 The environmental, economic and social footprint of concrete
2.2 Producing concrete with quarried aggregates
2.2.1 Ready-mix concrete
3 :: Step 2: Defining the New Business Case
3.1 The benefits of concrete recycling
3.2 Relevant European and national policy
3.2.1 The European Waste Framework Directive
3.2.2 The EU Construction and Demolition Waste Management Protocol
3.3 The French Energy Transition for Green Growth Act
3.4 Producing concrete with recycled aggregates
3.4.1 Quality concerns
4 :: Step 3: Changes in the Key Sector in France
4.1 The concrete sector
4.1.1 Cement industry
4.1.2 Aggregates industry
4.2 Scenario building
4.2.1 Key data and assumptions
4.2.2 Comparing the two scenarios
5 :: Step 4: Expected Effects on Other Parts of the French Economy
5.1 Total demand for aggregates
5.2 Construction sector
6 :: Step 5: The Impact on French Society
6.1 Possible disruptive effects
7 :: Step 6: Are Alternatives Available?
7.1 An increased use of other building materials
7.2 Reusing concrete in original form
8 :: Step 7: Policy Options
8.1 Enabling factors
8.1.1 European and national commitment
8.1.2 Improved CDW management
8.2 Barriers
8.2.1 Limited information on the pricing of CDW recycled materials
8.2.2 Little trust in the quality of CDW recycled materials
8.2.3 Lack of clarity on liability related to CDW recycled materials
8.3 Policies for consideration
8.3.1 Implementation of end-of-waste criteria for waste-derived aggregates
8.3.2 Landfill restrictions and taxes
8.3.3 Taxing quarried aggregates
9 :: Step 8: Overall Conclusions
9.1 Results
9.2 Policy recommendations
10 :: Technical Documentation
10.1 Measuring the different impacts
10.1.1 Environmental impacts
10.1.2 Numerical analysis
10.1.3 Interpolations of life-cycle assessment data
11 :: References
12 :: List of Partners - Keywords
-
France
Ecologic Institute 2016: CIRCULAR IMPACTS Online Library. URL: https://circular-impacts.eu/library
Conference:Impacts of the Circular Economy Transition in Europe – CIRCULAR IMPACTS Final Conference
- Date
-
- Location
- Brussels, Belgium
Rizos, Vasileios et. al. 2017: The Circular Economy. A Review of Definitions, Processes and Impacts.